To cool down, in an ideal world, we’d all just open a window or turn on a fan. When it’s hot, though, any form of cooling provides a welcome respite, especially at night when it’s too hot to sleep. Most individuals do not want to spend their summers hot, exhausted, and cranky.
With both evaporative and refrigerated cooling systems being powerful air conditioners providing great comfort, it is often a challenge to decide which system is right for you. With the continued rising temperatures over summer, it is never been such an important time as now to have the best AC possible!
What Is Evaporative Cooling?
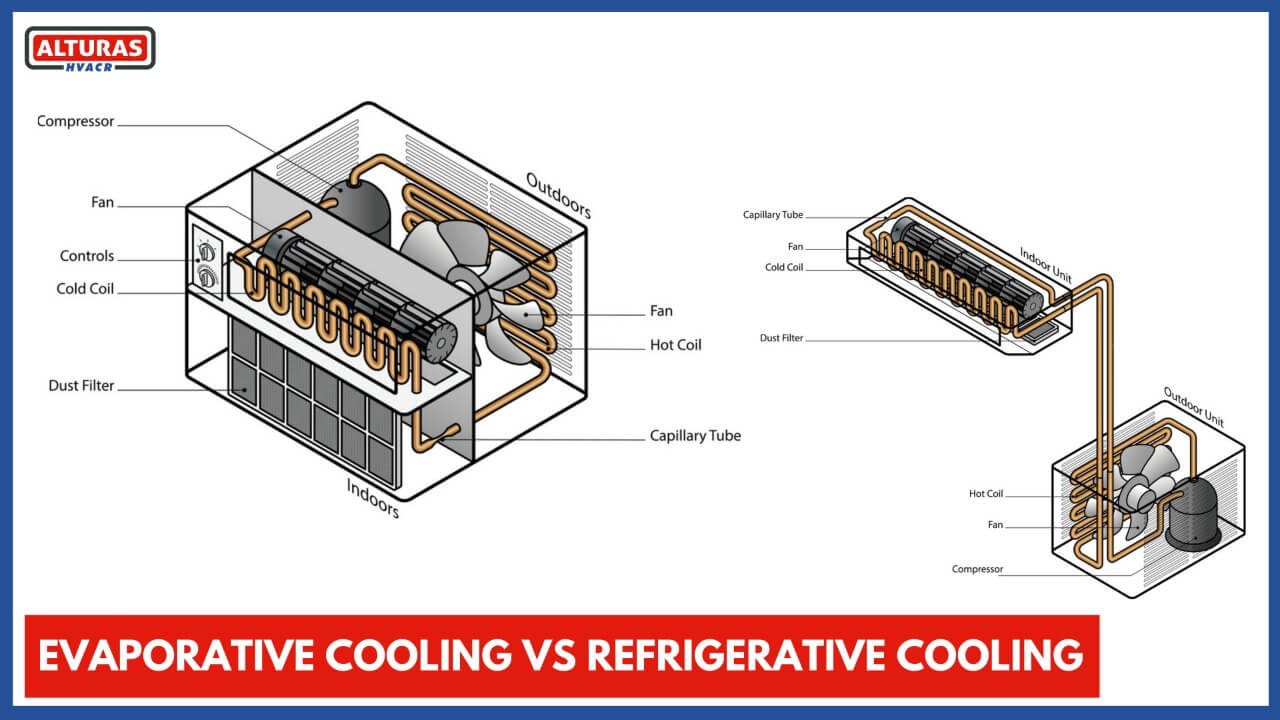
A central cooling unit is typically built on the top of your home and connected to a series of strategically arranged ceiling ducts using this sort of cooling system.
Warm air collected from outside is cooled by evaporation as it passes through the filters, thanks to a pump that pushes water from a reservoir onto filter pads or specially constructed cells in the unit. Cool air is subsequently sent throughout your home via ceiling ducts.
Windows and doors should be open throughout the house for evaporative cooling to work effectively.
What is Refrigerated Cooling?
Refrigerated cooling is a technology that uses a refrigeration system to remove heat from indoor air, creating a cooling effect. It involves the circulation of refrigerant to absorb and transfer heat, resulting in a comfortable and controlled indoor temperature.
How does refrigerated cooling work?
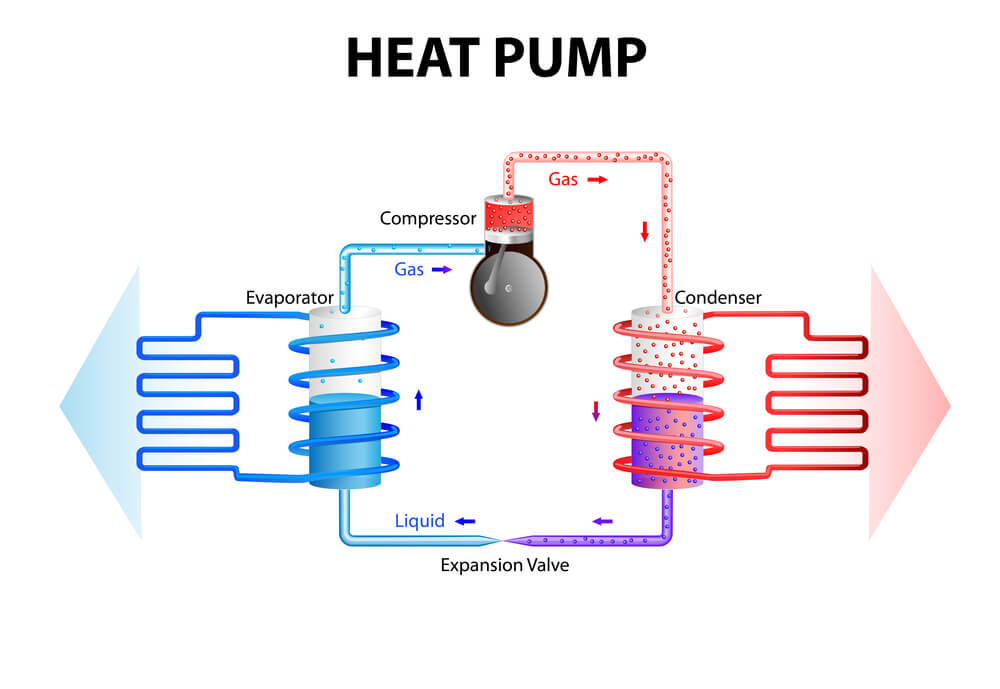
A refrigerated system removes hot air from space (such as your living room), cools it with refrigerant gases, and then returns the colder air to the space.
The outside condenser unit, where the refrigeration effect occurs, and the indoor fan coil unit, which comprises a heat exchange coil and fan, are the two components of these systems.
Windows and exterior doors must be closed for refrigerated refrigeration to work properly.
How does evaporative cooling work?
Evaporative cooling is a process that reduces air temperature by using the natural process of water evaporation. It works on the principle that when water evaporates, it absorbs a significant amount of heat from the surrounding air, thus lowering the air temperature.
Basic Components:
- Water Supply: Provides water to the system.
- Cooling Pads: Water is distributed over these pads, which are typically made of a material with a large surface area.
- Fan or Blower: Draws warm air from the outside, forces it through the wet cooling pads, and then circulates the cooled air into the indoor space.
Process:
- The water evaporates from the cooling pads, absorbing heat from the incoming air and cooling it down.
- The cooled air is then blown into the living space, while warm, humid air is pushed out of the building.
Which is better: Evaporative or Refrigerated cooling?
Let’s take a look at some of the benefits and drawbacks of each method.
Humid vs. dry climates
When it comes to evaporative cooling, living in lovely Melbourne gives you an advantage because the humidity is typically low. In hot and dry areas, evaporative systems operate best.
Evaporative cooling typically operates at temperatures of about 27°C, although the outside weather and the overall state of your system can affect performance.
A refrigerated system is required if you desire colder air.
Refrigerated systems will also give more dependable and effective cooling if you reside somewhere humid.
Cost to run
Evaporative coolers are far less expensive to operate than refrigerated systems by a wide margin.
Refrigerated conditioning is undoubtedly more dependable and effective, but it will result in a higher electricity cost during the hot summer months. Both systems will run more efficiently if your home is well-insulated.
When using evaporative systems, there’s an additional cost to consider: water.
Water usage rates are affected by the type of evaporative system you use, the area you live in, and the surrounding environment. You can inquire with Alturas about the amount of water you’ll use and your water provider about the amount of money you’ll be charged.
Air quality
Fresh air is continuously drawn in from the outside, filtered, cooled, and circulated throughout your home with evaporative systems. Because the air is never recirculated and is always fresh and clean, ‘stale’ air is never an issue.
The air is recirculated with chilled cooling. If someone in your house has a pollen allergy, this is frequently the best option. If your system isn’t properly maintained and the filters become clogged, recirculated air can become an issue. It will be stuffy and stale in the air.
The humidity of the air is another factor to consider. Refrigerated air is much dryer since it contains less moisture.
Environmental impact
Both systems consume electricity, but the refrigerated option consumes substantially more. Your best bet is to look for systems that are more energy-efficient and have a high “star rating.”
You might also want to consider the emissions produced by refrigerated cooling gases.
But don’t forget that evaporative systems use water, which has an impact on the environment.
Overall, the frequency with which you utilize the system will most likely be the most important element. For example, high-end, well-maintained refrigerated refrigeration utilized sparingly will likely have less impact than a whole-house evaporative system running 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Pros and Cons of Evaporative Cooling
Evaporative Cooler Pros
Evaporative coolers cool the air by adding humidity rather than removing it. In dry climates like Tucson’s, this can be useful. Too dry air can cause dry eyes, skin, and chapped lips, as well as warping or cracking of some household items (such as wood). A swamp cooler is also less expensive to buy, install, and run than a standard air conditioning system. Your energy expenses will be reduced if you use less electricity to chill your home. Evaporative coolers are also considered more environmentally beneficial if you’re concerned about the consequences of energy use on the environment.
Evaporative Cooler Cons
Evaporative coolers are effective in Tucson’s dry environment, but they have a few drawbacks. Air conditioners require less maintenance than evaporative coolers. Moisture buildup in your cooler can generate unpleasant odors and promote mold growth if it is not cleaned and maintained on a regular basis. Running an evaporative cooler consistently, which adds humidity to the air, can make your home feel sticky and uncomfortable, rather than improving it. Furthermore, to ensure effective cooling, evaporative coolers require a constant supply of water. If you have a large evaporative cooler or need to run it constantly to maintain a comfortable interior atmosphere, the greater cost of water in desert areas can be prohibitive.
Pros and Cons of Refrigerated Cooling
Refrigerated cooling, commonly known as air conditioning or mechanical refrigeration, is a process used to lower the temperature of a space by removing heat. This method is widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Here are some of the pros and cons of refrigerated cooling:
Pros
- Effective Cooling:
- Provides precise temperature control and can lower temperatures significantly, making it ideal for hot climates or areas with high humidity.
- Humidity Control:
- Reduces humidity in the air, which can help prevent mold growth and improve comfort.
- Air Quality:
- Many systems come with air filters that can improve indoor air quality by removing dust, allergens, and other pollutants.
- Comfort:
- Creates a comfortable living or working environment, which can improve productivity and overall well-being.
- Versatility:
- Can be used in various settings, from small rooms to large buildings, and can be customized to meet specific cooling needs.
- Year-Round Use:
- Many systems offer heating options as well, making them useful throughout the year.
Cons
- High Energy Consumption:
- Refrigerated cooling systems can consume a significant amount of electricity, leading to higher energy bills and environmental impact.
- Initial Cost:
- The installation and purchase of air conditioning systems can be expensive, especially for high-efficiency models or large spaces.
- Maintenance Requirements:
- Requires regular maintenance to ensure efficiency and longevity. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased performance and higher energy consumption.
- Environmental Impact:
- The refrigerants used in some systems can contribute to global warming if not properly managed. Newer systems use more environmentally friendly refrigerants, but older models may still pose a risk.
- Noise:
- Some air conditioning units can be noisy, which may be a concern in quiet environments like bedrooms or offices.
- Health Concerns:
- Poorly maintained systems can become breeding grounds for bacteria and mold, leading to potential health issues for occupants.
- Dependency:
- In regions where refrigerated cooling is widely used, people may become overly dependent on it, potentially leading to discomfort or health issues when it’s unavailable.
FAQs (Evaporative cooling vs Refrigerated cooling)
Can you change evaporative cooling to refrigerated cooling?
Yes, you can. This is what we call an evaporative changeover. Changing over from evaporative to reverse cycle refrigerated ducted air conditioning is a simple task that is often completed in 1 day.
What are the drawbacks of evaporative cooling?
Because it adds humidity to the air, running your evaporative cooler constantly can cause your home feel sticky and less comfortable, rather than improving comfort. Additionally, evaporative coolers require a steady supply of water to maintain adequate cooling.
Is evaporative cooling better?
It’s better for the environment. An evaporative unit emits less carbon dioxide and uses a more natural process to keep your home cool. Therefore, you’re able to keep your home comfortable without leaving a big carbon footprint
Do you keep windows open with evaporative cooling?
For evaporative cooling to be the most efficient, and to use the cleanest air, it is important to keep your windows open so that the evaporative system can filter through fresh air.